Online thermal desorption aerosol mass spectrometers (TDAMS) provide useful insights into the sources and formation processes of ambient aerosols. TDAMS instruments generally use a two-step detection scheme: aerosol particles are first collected and vaporized by thermochemical processes in a vacuum chamber, following which the evolved gaseous compounds are ionized and then detected. We have developed a new particle mass spectrometer (rTDMS) to separately quantify the mass concentrations of non-refractory and refractory sulfate compounds1. A cup-shaped graphite collector coupled with a focused CO2 laser enables high desorption temperature (~1200 K). Laboratory experiments have demonstrated that the rTDMS can detect ion signals originating from refractory sulfate aerosols including K2SO4, Na2SO4, and MgSO4 (Fig. 1).
The reaction of sea salt (or biomass burning) particles with sulfuric acid and nitric acid leads to the displacement of chloride relative to sodium (or potassium). We have proposed a new method to quantify the mass concentrations of sodium nitrate (NaNO3), sodium chloride (NaCl), sodium sulfate (Na2SO4), potassium nitrate (KNO3), potassium chloride (KCl), and potassium sulfate (K2SO4) particles by using the rTDMS2. Laboratory experiments showed that temporal profiles of ion signals at m/z 23 (or 39) originating from multi-component sodium (or potassium) salt particles were characterized by three sequential peaks associated with the evolution of the desorption temperature. Improvements of the rTDMS for ambient measurements of aerosol particles are now ongoing.
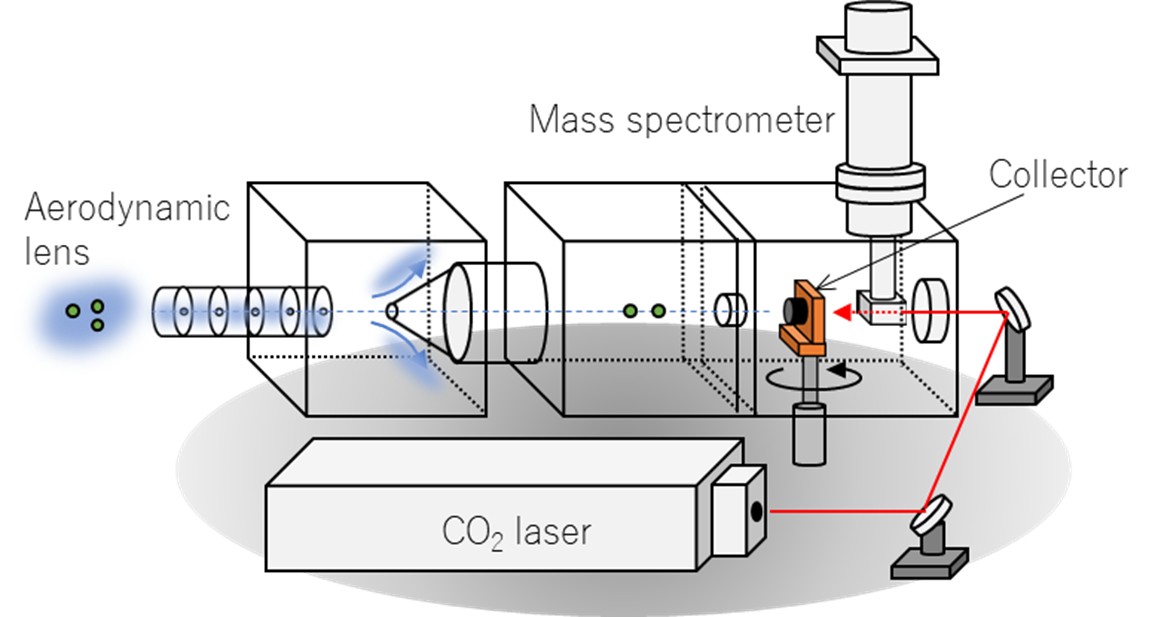
Fig. 1. Schematic view of a new particle mass spectrometer (rTDMS).
References
-
Kobayashi, Y., Ide, Y., and Takegawa, N., Development of a novel particle mass spectrometer for online measurements of refractory sulfate aerosols, Aerosol Sci. Technol., 55, 371–386, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1080/02786826.2020.1852168
-
Kobayashi, Y. and Takegawa, N., A new method to quantify particulate sodium and potassium salts (nitrate, chloride, and sulfate) by thermal desorption aerosol mass spectrometry, Atmos. Meas. Tech., 15, 833–844, 2022. https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-15-833-2022